The quest for increasingly healthy meals and food has resulted in a trend favouring vegetarian foods and vegan formulations. In this article, we analyse consumer motivations for seeking plant-based foods, their various trends, and the strategies being employed by the food industry to develop new formulations that can meet the needs of the growing ‘green’ demand.
An analysis of the depth of the ‘veggie’ trend
Consumers worldwide are increasingly opting to reduce the consumption of animal meat in their diets in favor of increasing vegetable intake, a trend known as flexitarianism. Others, such as vegans and vegetarians, completely eliminate meat consumption from their diets.
According to data from the consulting firm Mintel, 50 million vegetarians live in China, with 80% of the population in India abstaining from meat for religious reasons. In the United States, 10% of surveyed adults claim to follow a vegetarian diet. In Europe, 7.7 million Germans identify as vegetarian, and 12% of adults in the United Kingdom adhere to a vegetarian or vegan diet, with this percentage increasing among young people aged 16 to 24 to 20%.
Spain is also following the trend. According to “The Green Revolution” report by Lantern consulting firm, 6.3% of Spaniards are flexitarians, 1.3% are vegetarian, and 0.2% lean towards a vegan diet. Together, they account for approximately 3.6 million Spaniards, roughly 7.8% of our country’s population. But what are the reasons motivating the adoption of ‘veggie’ diets?
According to Mintel’s “Nutrition Insight: Vegans/Vegetarians/Flexitarians” report, the current consumer adoption of vegan and vegetarian diets goes beyond ethical reasons and responds to a specific consumer need for more natural, sustainable, and above all, healthier foods, often free from certain allergens such as eggs and milk.
Innovation satisfying the demand for vegan and vegetarian products
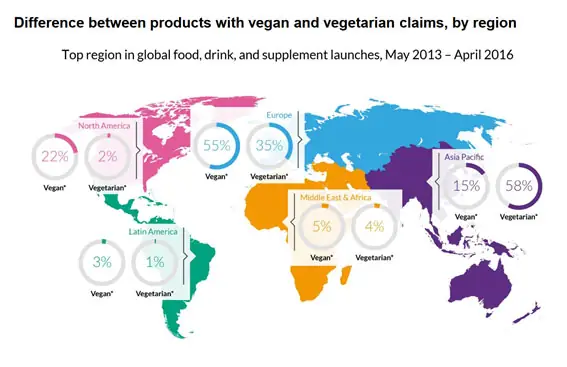
According to Mintel in their 2017 Food & Drink Trends study, Europe leads the launch of new foods that include vegan claims or statements. A trend that has increased worldwide by 257%.
Differences between vegan and vegetarian claims in product launches by region from 2013 to April 2016. Source: “Nutrition Insight: Vegans/Vegetarians/Flexitarians,” June 2016. Mintel GNPD
According to the consulting firm, bakery products and snacks are the categories that have seen the most launches of this kind. Snacks, in particular, innovate by incorporating cereals, nuts, and seeds into their recipes. Among them, snack bars stand out for their ability to provide nutritional and energy benefits, offering a healthy alternative.
Additionally, the market for supplements or fortified foods aimed specifically at vegetarian and vegan consumers is growing. These launches are designed to meet the new dietary and nutritional needs such as amino acids, essential fatty acids, vitamin D, vitamin B12, etc., which are typically obtained from meat and fish.
Looking for meat substitutes
In the article “Alternative Sources of Proteins: Where is Food Innovation Heading?”, we discussed the characteristics of a trend that is consolidating in the search for meat substitutes. These substitutes not only match the protein levels of meat but also mimic its texture, flavor, color, and role as an ingredient in new recipes.
According to Mintel, soy is one of the top 10 products preferred by the food industry as meat substitutes. In fact, the consultant states that 44% of launches include soy, an ingredient capable of replacing meat with products based on tofu and tempeh.
For protein supplementation, soy is also an interesting alternative adopted by the industry. In fact, among the most commonly used plant proteins are soy and wheat. Pea proteins, on the other hand, serve as an alternative to allergens found in soy and wheat.
Among emerging foods, Mintel highlights legumes, seeds, ancient grains and cereals, and nuts for their potential as meat substitutes. At AINIA, we’ve discussed all of them, their properties, and market penetration in the article “Superfoods: Food and Health All in One.” (Spanish)
We can’t conclude this overview of ingredients presented as meat substitutes for their nutritional and protein content without mentioning microalgae. Spirulina and chlorella, whose potential we analyzed in the article “The Potential of Microalgae Spirulina and Chlorella in Food,” (spanish) contain a high percentage of easily digestible and assimilable amino acids. In fact, these microalgae are the foundation of the A4HW project, in which AINIA participates, aiming to develop superfoods from microalgae cultivated using an electric power plant.
However, it’s important to highlight a significant aspect regarding the formulations of new plant-based foods as meat substitutes. Mintel warns that a significant percentage of consumers (42% in the US) believe that these types of foods are overly processed, and 72% of them place great importance on knowing what they are made of.
If you want to seize the opportunity presented by the “veggie” trend to innovate in the development of new vegetarian foods, get in touch with AINIA. We can assist you throughout the entire process.